Welding
Incorporate welding for robust connections, enhancing structural integrity and durability, ensuring a seamless and reliable integration of components in your product.
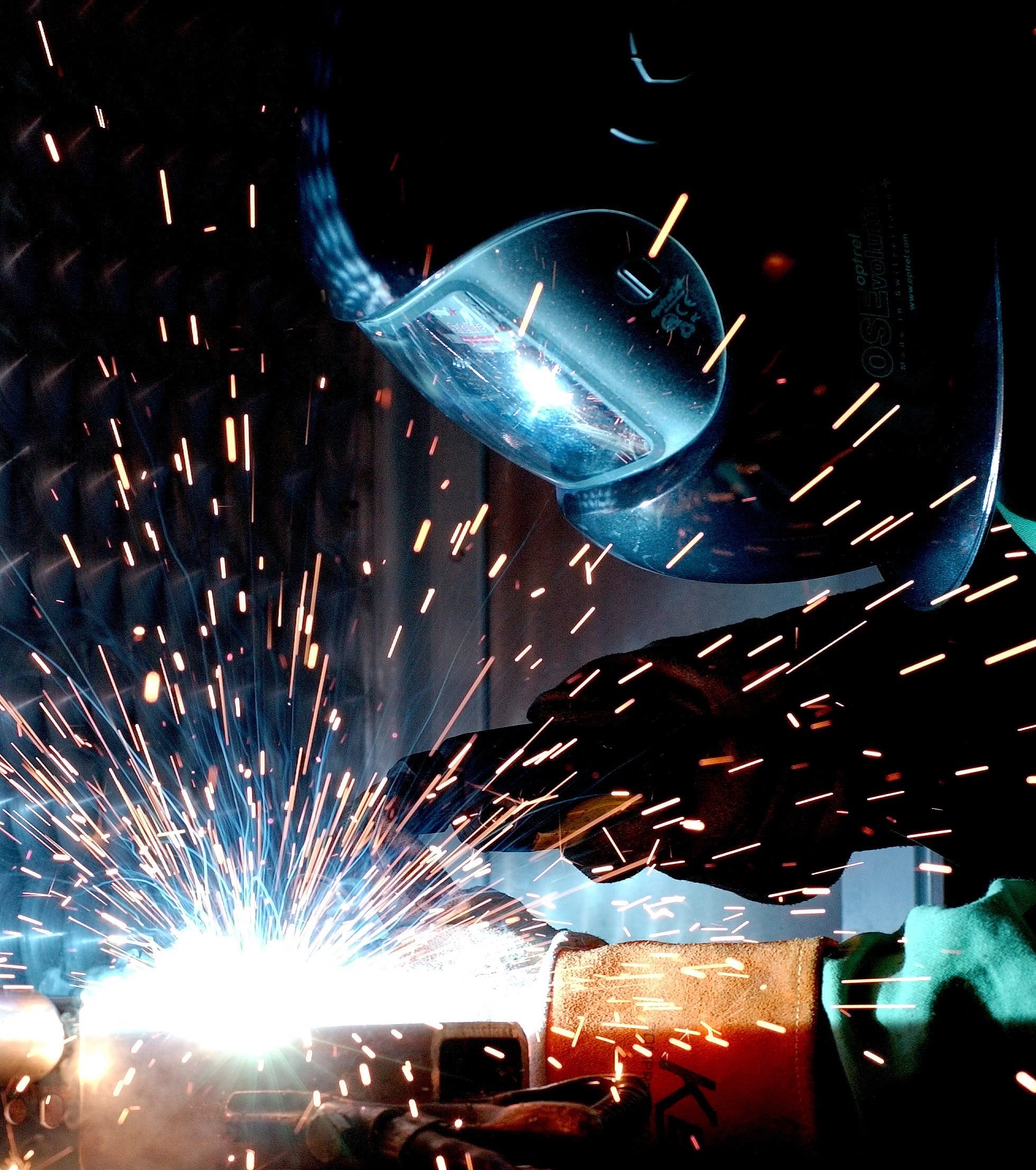

Incorporate welding for robust connections, enhancing structural integrity and durability, ensuring a seamless and reliable integration of components in your product.

Welding, a process of joining materials, typically metals, involves fusing them together through heat and pressure. In the arc welding method, an electric arc forms between the welding electrode and the workpieces, generating intense heat to melt the materials. As the molten metal cools, a robust and permanent bond is established. This versatile fusion process accommodates various techniques such as MIG, TIG, and stick welding, each providing specific advantages based on materials and application needs. Skilled welders, applying their art, play a crucial role in achieving precise and reliable welds.
A wide range of materials can be welded, with the most common being metals. The materials suitable for welding include:
The most significant advantage of welding in industry lies in its ability to create strong and durable connections. Welding produces robust and permanent joints, ensuring the structural integrity of assembled components. This strength is crucial in industrial applications where reliability and durability are paramount. The capability of welding to forge enduring connections makes it indispensable in various industries, ranging from construction and automotive to aerospace and manufacturing, where the resilience of joints is critical for the overall performance and safety of the final products.